3240-B Epoxy Phenolic Glass Cloth Laminated Sheet: Performance, Standards, and Industrial Applications
Introduction
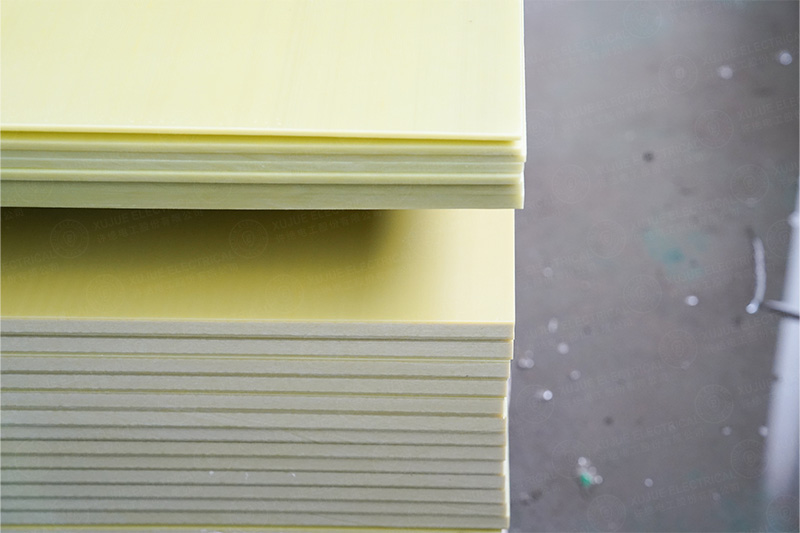
The 3240-B epoxy phenolic glass cloth laminated sheet is a high-performance insulation material widely applied in dry-type transformers, electric motors, switchgear, and automation equipment.
It is produced by laminating alkali-free glass fabric impregnated with modified epoxy phenolic resin, providing high dielectric strength, mechanical rigidity, and thermal stability up to Class F (155°C).
According to GB/T 3240-2017 and IEC 60893, this material meets strict standards for electrical insulation boards used in medium-voltage and mechanical systems.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
3240-B consists of multiple layers of woven E-glass cloth bonded with epoxy phenolic resin through a high-temperature hot-pressing process (≥160°C, ≥6 MPa).
The combination of epoxy resin (for adhesion and strength) and phenolic resin (for thermal and chemical stability) results in a composite that maintains dimensional accuracy and insulation reliability even in humid or high-temperature environments.

Performance and Technical Data
1. Electrical Insulation Properties
3240-B demonstrates stable dielectric characteristics under voltage and thermal load.
Dielectric strength: ≥14 kV/mm (IEC 60243-1)
Insulation resistance: ≥1.0×10¹² Ω (IEC 60093)
Dielectric constant (1 MHz): 4.8–5.5
These values confirm its suitability for electrical insulation sheet GB/T 3240 applications such as transformer spacers and phase barriers.
2. Mechanical Properties
Its high glass-fiber reinforcement ensures excellent mechanical integrity:
Flexural strength: ≥340 MPa (GB/T 5130-2019)
Compressive strength: ≥300 MPa
Impact strength: ≥33 kJ/m²
These figures allow it to function effectively in epoxy glass cloth insulation board roles such as load-bearing supports and insulating fixtures.
3. Thermal Endurance
Classified as Class B insulation material, 3240-B maintains strength and insulation up to 130°C continuous operation.
Thermal aging tests (IEC 60216) show that it retains >80% mechanical strength after 1000 hours at 125°C, outperforming ordinary phenolic sheets.
4. Moisture and Chemical Resistance
With water absorption <0.5%, 3240-B performs reliably in oil-immersed and humid environments.
It resists transformer oil, organic solvents, and alkaline cleaning agents — a critical feature for Class B insulation material for transformers.
Applications
1. Transformers
Used as: Support plate, phase barrier, oil duct strip, and clamping block.
Advantages: Excellent heat resistance, no deformation, stable dielectric strength under long-term load.
2. Motors
Used as: Slot wedges, end plates, insulating spacers.
Benefits: Strong mechanical rigidity, vibration resistance, and thermal endurance for Class B motor insulation systems.
3. Control & Power Equipment
Applied in switchboards, relays, circuit breakers, and electrical cabinets where combined structural and electrical insulation is required.
4. Mechanical and Tooling Applications
• Ideal for fixtures, jigs, and molds operating in heat and stress conditions.
• Can be machined easily via CNC or drilling without delamination.
Processing and Handling Recommendations
• To achieve optimal results:
• Use carbide or diamond-coated cutters to avoid fraying or delamination.
• Maintain feed speed at 100–150 mm/min to prevent overheating.
• Pre-dry sheets at 80–100°C for 2–3 hours before machining in high-humidity environments.
• Edge sealing is recommended for components exposed to oil or moisture.
Conclusion
The 3240-B epoxy phenolic glass cloth laminated sheet provides a balanced combination of mechanical strength, dielectric reliability, and Class B thermal performance.
Its compliance with GB/T 3240 and IEC 60893 ensures consistent quality across international markets.
For applications requiring durable, precise, and cost-effective insulation — such as transformers, motors, and automation systems — 3240-B remains one of the most trusted epoxy phenolic laminate properties solutions in industrial insulation engineering.