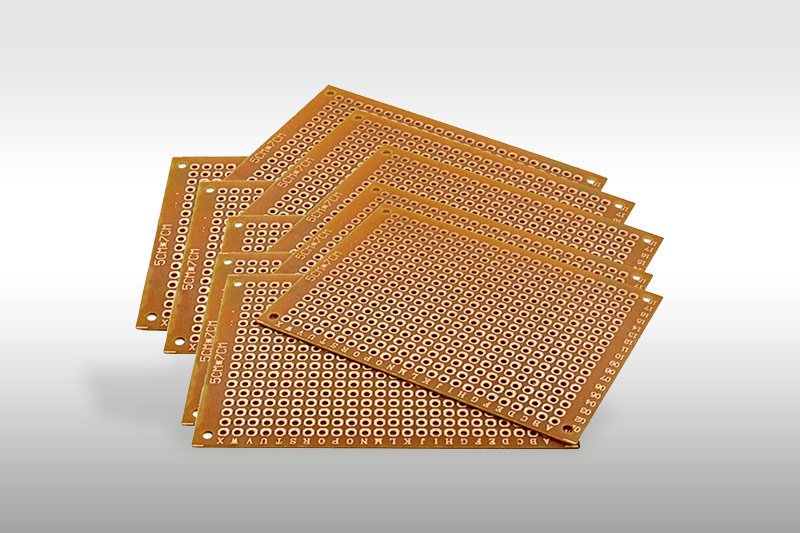
Epoxy Fiberglass Sheets (FR4, G10, G11): A Practical Guide for Electrical Insulation Applications
Epoxy fiberglass sheets are widely used across electrical and industrial systems, including transformers, motors, switchgear, and power distribution equipment.
Commonly known grades such as FR4, G10, and G11 are often grouped together as “epoxy insulation boards,” but in real-world applications, their performance differences directly affect equipment reliability, service life, and procurement risk.
This article explains how epoxy fiberglass laminates function beyond basic insulation and how to select the right material for long-term electrical performance.
What Are Epoxy Fiberglass Sheets?
Epoxy fiberglass sheets are laminated composite materials made by impregnating woven fiberglass cloth with epoxy resin, followed by curing under high temperature and pressure.
Key properties include:
• High dielectric strength and electrical insulation performance
• Excellent mechanical strength and dimensional stability
• Resistance to moisture, chemicals, and environmental aging
• Stable performance under long-term electrical and thermal stress
Because of this balance, epoxy fiberglass laminates are commonly specified for structural insulation components rather than simple isolation layers.
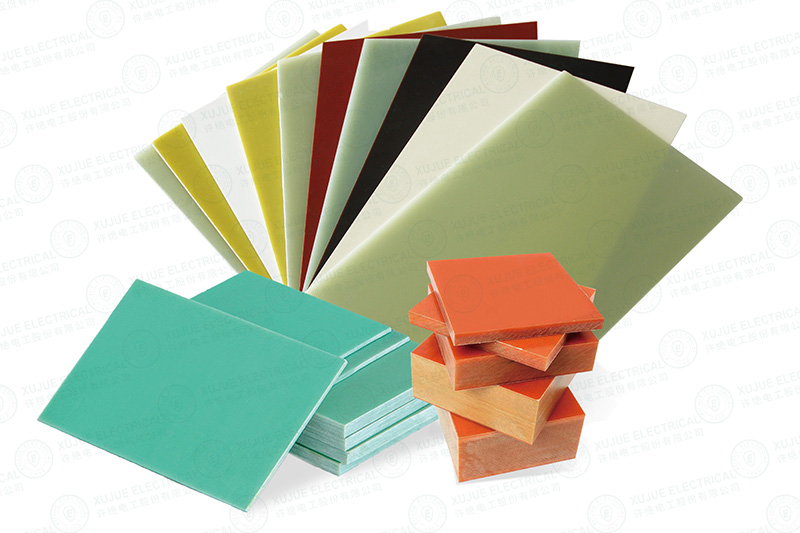

Applications of Epoxy Fiberglass Insulation Boards
Epoxy fiberglass sheets are widely used in:
• Power transformers and dry-type transformers
• Electric motors and generators
• Switchgear and high-voltage electrical cabinets
• Busbar supports and insulation spacers
• Electrical equipment requiring both insulation and mechanical load-bearing
In these applications, epoxy boards often function as critical structural insulation materials, meaning material quality consistency is just as important as initial specifications.
FR4 vs G10 vs G11: Key Differences Explained
Although FR4, G10, and G11 share similar compositions, they are not interchangeable.
FR4 Epoxy Fiberglass Sheet
FR4 is commonly selected for applications requiring reliable electrical insulation with balanced cost efficiency. It is widely used in PCB laminates and general electrical insulation parts.
G10 Epoxy Fiberglass Sheet
G10 offers higher mechanical strength and improved dimensional stability. It is preferred in applications involving mechanical stress, vibration, or structural support.
G11 Epoxy Fiberglass Sheet
G11 is designed for higher thermal resistance and continuous operation in elevated temperature environments. It is commonly used in motors, transformers, and equipment operating under long-term heat load.
Selecting the wrong grade may reduce upfront cost but increases long-term operational risk.
Key Factors When Sourcing Epoxy Fiberglass Sheets
From a procurement and engineering perspective, the biggest risks are material inconsistency and application mismatch, not unit price.
Important evaluation factors include:
• Uniform resin impregnation and curing quality
• Thickness tolerance and flatness consistency
• Long-term thermal aging performance
• Electrical stability under continuous voltage stress
• Supplier quality control and batch traceability
A reliable epoxy fiberglass sheet manufacturer should provide not only materials but also technical guidance and stable long-term supply.
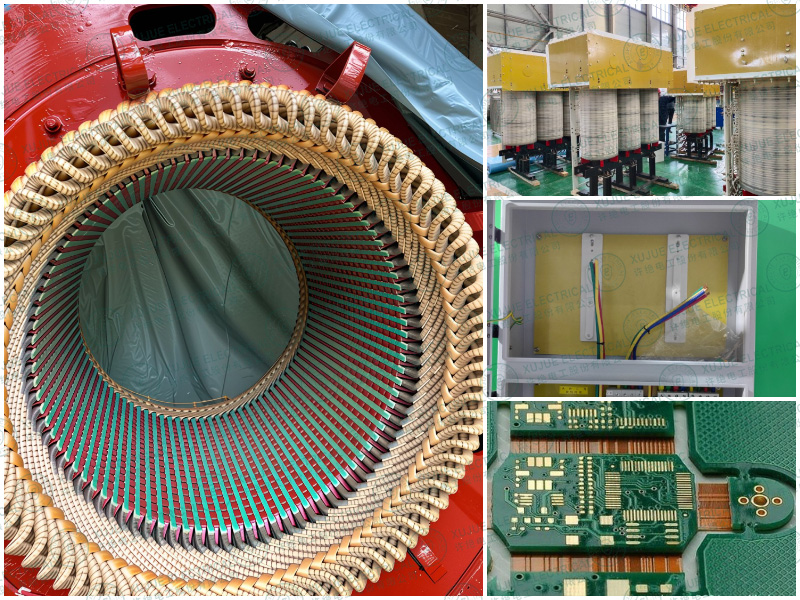
Why Material Selection Impacts Electrical System Reliability
In electrical systems, insulation materials are the foundation of safety and reliability.
Poor-quality epoxy fiberglass boards may lead to insulation degradation, mechanical deformation, or partial discharge risks over time.
Choosing the correct epoxy fiberglass sheet grade helps reduce maintenance costs, extend equipment lifespan, and improve overall system stability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Epoxy Fiberglass Sheet for Your Application
Epoxy fiberglass sheets such as FR4, G10, and G11 are more than standard laminates.
They are engineering materials that directly influence electrical performance and long-term reliability.
Understanding material differences, application requirements, and supplier capability is essential for making informed sourcing decisions in electrical insulation projects.